- Home Page
- Company Profile
-
Our Products
- Hydraulic Pumps
- Hydraulic Solenoid Valves
- Conventional Valves
- Proportional Valves
- Safety Valves
- Mobile Control Valves
- Hydraulic Motor
- Cylinders and Servo Cylinders
- Hydraulic Filters
- Hoses and Fittings
- Gates Hydraulic Hose
- MP Filters Filters
- Dowty Gear Pumps
- Polyhydron Valves
- Manifold Blocks
- Walvoil
- Spica
- Hand Pumps
- ATOS Hydraulic Components
- Blog

Best Metallurgical Bridge Crane Types for Efficient Operations?
Efficient operations in metallurgical processes depend on the right equipment. Among these, the Metallurgical Bridge Crane plays a crucial role. This crane type is designed specifically for heavy-duty tasks in steel mills and foundries. Its robust structure supports the handling of molten metal and large materials.
Different types of Metallurgical Bridge Cranes exist. Each offers unique features tailored to specific operational needs. Some may prioritize speed, while others focus on lifting capacity or precision. Understanding these variations can enhance productivity.
However, selecting the optimal Metallurgical Bridge Crane isn’t always straightforward. Factors like workspace dimensions, load types, and safety standards must be considered. A poorly chosen crane can lead to inefficiencies. Organizations must invest time in research and consultation. This decision impacts not only productivity but also employee safety and operational reliability.
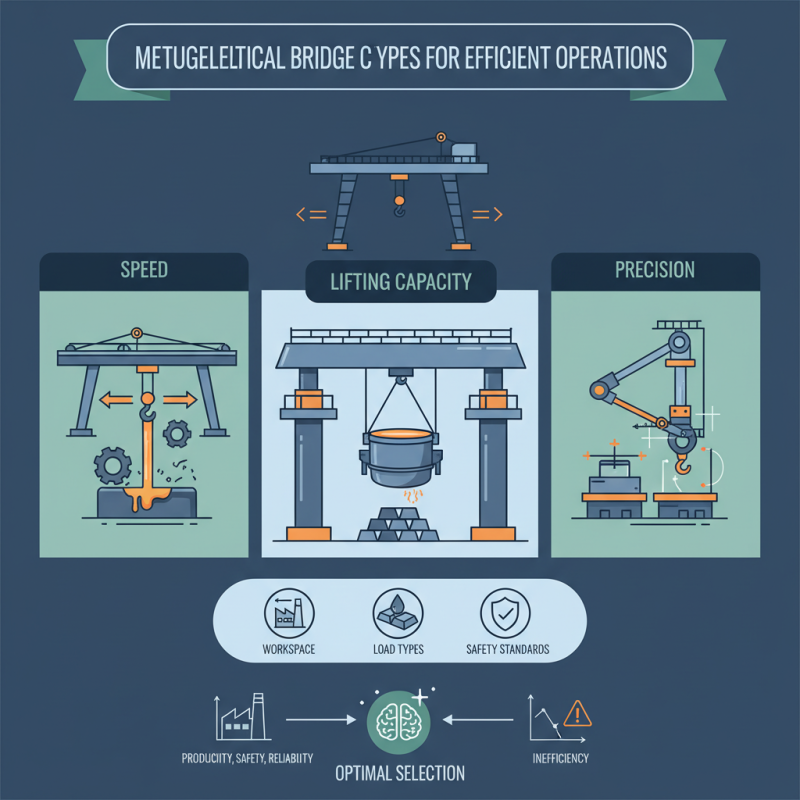
Overview of Metallurgical Bridge Cranes and Their Importance
Metallurgical bridge cranes play a significant role in heavy industry. They are crucial for handling and transporting steel, metal sheets, and other heavy materials. The design of these cranes is tailored for durability and efficiency, making them suitable for rigorous operations.
In metallurgical settings, safety is paramount. These cranes often operate in challenging environments with high temperatures and heavy loads. This requires careful maintenance procedures to avoid accidents. Operators must be trained to recognize potential hazards and to respond effectively. Equipment failure can lead to costly downtime and dangerous situations.
Operators often face challenges in optimizing crane performance. Load balance is critical but can be tricky. Miscalculating load weights can lead to issues. Regular monitoring is necessary to ensure optimal function. Reflecting on past operations can inform better practices.
Overview of Metallurgical Bridge Cranes Performance Metrics
Key Types of Metallurgical Bridge Cranes for Heavy Lifting
Metallurgical bridge cranes are essential for heavy lifting in industrial environments. Their design allows them to handle large loads efficiently. Some common types include the single girder and double girder cranes. Each type has unique advantages. For example, single girder cranes are often lighter and more cost-effective. However, they may not support as much weight as double girder cranes.
Double girder cranes stand out in heavy-duty lifting. They provide better support and stability. This makes them ideal for factories with heavy machinery. Operators need to consider the capacity carefully. Misjudging load limits can lead to accidents. The balance of weight distribution is crucial.
Other types to consider are overhead and gantry cranes. Overhead cranes work well in enclosed spaces. Gantry cranes are more versatile, often used outdoors. However, both types require proper training for operators. Understanding the mechanics is vital. Without this, the operation could become dangerous. Each crane type has strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the right one is essential for efficiency.
Features and Specifications of Effective Bridge Cranes
When choosing a bridge crane for metallurgical operations, several features are essential for improved efficiency. High lifting capacities are crucial. Cranes typically range from 5 tons to over 100 tons. This allows them to handle heavy materials with ease.
Low headroom designs maximize vertical space, which is often limited in industrial settings. This design helps in creating more usable area below the crane.
The control systems also play a significant role in crane operations. Modern bridge cranes often incorporate advanced control systems. These systems provide precision in maneuvering heavy loads. Ergonomic controls enhance operator comfort, reducing fatigue. It’s vital to consider these elements for safety and productivity. Overlooked aspects can lead to operational inefficiencies.
Material durability is another key specification. Steel construction is common, but not all steel types are equal. Some may corrode easily or wear out faster. Also, the environmental conditions should influence your choice. Extreme temperatures can affect crane performance. Therefore, understanding specific operational needs is necessary for long-term efficiency.
Factors Influencing the Choice of Bridge Crane Type
When selecting a metallurgical bridge crane, several factors play a crucial role in making the best choice. Load capacity is essential. Cranes designed for heavy loads can manage materials efficiently. According to industry studies, cranes with a load capacity of 25 tons are popular in steel production facilities. This allows for safe transport and minimizes the risk of accidents.
Another important consideration is the operational environment. Factors such as temperature and humidity can affect crane performance. For instance, in extreme conditions, specialized materials may be required. Reports indicate that cranes operating in high-temperature areas can achieve up to 10% more efficiency with appropriate modifications.
Finally, the ease of maintenance should not be overlooked. Regular maintenance schedules help prevent unexpected downtimes. Yet, many facilities still face challenges in this area. A study showed that around 30% of crane failures were due to inadequate maintenance practices. Reflecting on these aspects can lead to better long-term performance and operational efficiency in metallurgical processes.
Best Practices for Optimizing Bridge Crane Operations in Metallurgy
Optimizing bridge crane operations in metallurgy is essential for improving efficiency. According to a recent industry report, well-optimized crane systems can enhance productivity by up to 30%. Effective training programs for operators can significantly reduce errors and accidents, leading to safer operations.
Key best practices include routine maintenance checks. A proactive maintenance schedule can minimize downtime. An alarming statistic shows that over 40% of crane failures stem from neglect. Operators should regularly inspect vital components to ensure reliability.
Another significant factor is the load management technique. Proper load distribution minimizes strain on the equipment. Mismanaged loads can slow operations. Data indicates that cranes often operate below their safe capacities, risking potential failures. This highlights the need for operators to be well-versed in load calculations.
Article Source:
Developed and Managed byInfocom Network Private Limited.
 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry
