- Home Page
- Company Profile
-
Our Products
- Hydraulic Pumps
- Hydraulic Solenoid Valves
- Conventional Valves
- Proportional Valves
- Safety Valves
- Mobile Control Valves
- Hydraulic Motor
- Cylinders and Servo Cylinders
- Hydraulic Filters
- Hoses and Fittings
- Gates Hydraulic Hose
- MP Filters Filters
- Dowty Gear Pumps
- Polyhydron Valves
- Manifold Blocks
- Walvoil
- Spica
- Hand Pumps
- ATOS Hydraulic Components
- Blog

What is a Coaxial Attenuator and How Does It Work?
The world of signal processing hinges on the effective use of devices like the Coaxial Attenuator. This component is essential for managing signal strength in various applications, from telecommunications to audio devices. Peter Johnson, a renowned expert in RF engineering, once stated, "The Coaxial Attenuator is a silent hero in maintaining signal integrity.”
Understanding how a Coaxial Attenuator functions can help demystify its vital role in communication systems. Essentially, it reduces signal power without distorting signal quality. The attenuation is achieved through resistive networks, which absorb excess energy. Yet, not all attenuators are created equal.
In practical applications, choosing the right Coaxial Attenuator can be challenging. Variations in frequency response, power rating, and insertion loss are common concerns. Decision-makers must reflect carefully on these factors. The implications of selecting an inappropriate attenuator can lead to performance issues. This highlights the importance of precise engineering and application knowledge.
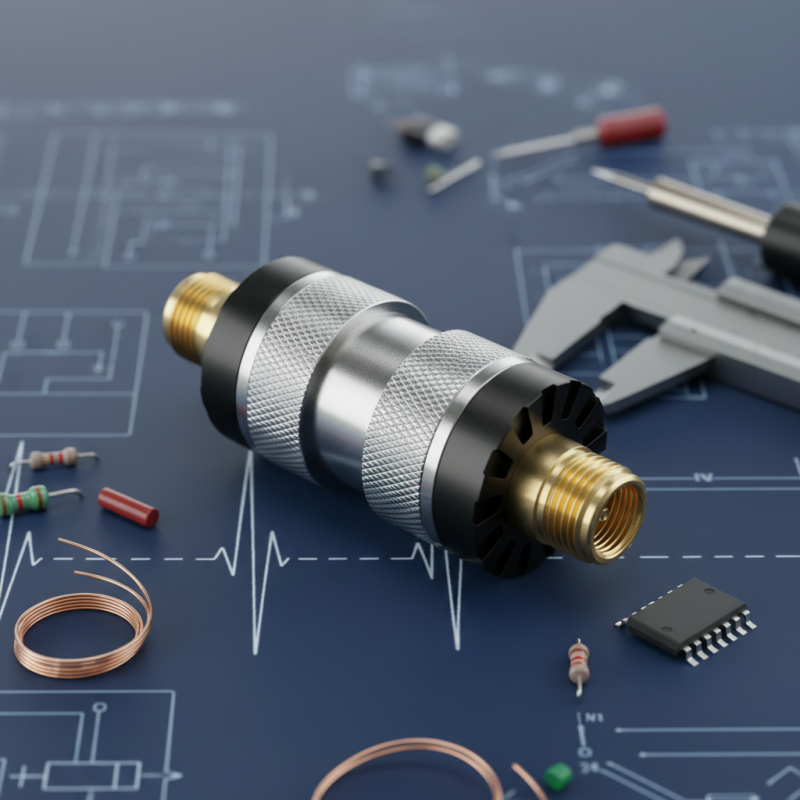

Definition of a Coaxial Attenuator and Its Purpose
A coaxial attenuator is an essential device in many communication systems. It plays a crucial role in managing signal strength. The main purpose of an attenuator is to reduce the power of the incoming signal. This helps to prevent overloads and distortion in sensitive equipment. According to industry reports, proper signal management can improve the overall performance of RF systems significantly.
The design of a coaxial attenuator usually involves resistive elements. These elements are fine-tuned to achieve specific levels of attenuation. For example, a common value for attenuation is 10 dB, suitable for standard applications. However, attenuators can range from 1 dB to 30 dB depending on the needs. While many systems benefit from using these devices, the choice of attenuation level is often a point of contention among engineers. Balancing signal quality and performance is a delicate task that requires careful consideration.
Issues can arise if the chosen attenuator is not appropriate. Too much attenuation can lead to inadequate signal strength. Too little may not protect against distortion. It’s important to critically evaluate the system requirements before making a decision. Reports indicate that a significant percentage of system failures relate to improper signal management. Thus, understanding the function of coaxial attenuators is essential for optimizing network performance.
Principles of Operation for Coaxial Attenuators
Coaxial attenuators are essential components in various electronic systems. They help manage signal levels within a coaxial cable setup. Understanding how they work can improve system performance significantly. The attenuation process relies on resistive elements. These resistors dissipate power, converting it into heat. Consequently, the output signal is weaker compared to its input.
The principles of operation for coaxial attenuators are quite straightforward, but implementation can be tricky. When a signal passes through an attenuator, it encounters these resistors. The design ensures that the signal integrity is preserved while reducing the signal strength. Sometimes, choosing the wrong attenuation level can lead to performance issues. This requires careful planning and calculations.
In practice, the connectors and materials used make a real difference. Quality coaxial cable and connectors are vital. Poor choices can cause unnecessary signal loss. An attenuator’s role becomes clearer when observing signal flow. It’s easy to overlook these components, yet they are crucial for optimal performance. Fine-tuning these elements is important for achieving the desired results.
Coaxial Attenuator Performance Overview
This chart illustrates the performance of coaxial attenuators at various attenuation levels measured in decibels (dB). As the input attenuation increases, the output signal experiences a corresponding reduction in amplitude, showcasing the effectiveness of the attenuators in controlling signal strength.
Types of Coaxial Attenuators and Their Applications
Coaxial attenuators are essential for managing signal integrity. They help control signal power levels. Different types cater to various needs. Understanding their applications is crucial.
There are fixed attenuators, which reduce signal power by a set amount. They work well in stable environments. Variable attenuators allow adjustment, providing flexibility in signal control. These are often used in testing. The choice depends on your requirements.
Tips: Ensure you select the right attenuator type for your application. Mismatched components can lead to signal degradation. Installation should be neat and secure, as loose connections can introduce noise. Regular checks can prevent unexpected issues. Proper setup leads to better performance overall.
Coaxial Attenuator Types and Applications
| Type | Attenuation (dB) | Frequency Range (GHz) | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Attenuator | 1 - 30 | DC - 18 | Signal Level Adjustment |
| Variable Attenuator | 0 - 30 | DC - 6 | Dynamic Signal Control |
| Step Attenuator | 1, 2, 3, 6, 10, 20 | DC - 18 | Testing and Measurement |
| Attenuator Pad | 1 - 20 | DC - 12 | Power Splitting |
Factors Affecting Coaxial Attenuator Performance
When dealing with coaxial attenuators, several factors influence their performance. One important element is frequency response. The attenuation level varies at different frequencies, impacting signal quality. Higher frequencies often experience more loss. This variability can be challenging for engineers seeking consistent performance across a range of applications.
Temperature can also affect attenuator functionality. Heat can lead to changes in resistance, altering the attenuation characteristics. It’s crucial to monitor operating temperatures. If an attenuator overheats, it might not perform as expected. This is often overlooked in design considerations, leading to frustrating results in practical use.
Additionally, the quality of the materials used in construction matters greatly. High-quality materials yield better performance. However, some manufacturers cut costs, which can compromise effectiveness. Users are sometimes left questioning their choices in these situations. Balancing cost and quality is a persistent challenge in the industry. Proper understanding of these factors is essential for achieving optimal performance from coaxial attenuators.
Installation and Maintenance Tips for Coaxial Attenuators
Coaxial attenuators are essential for managing signal levels in various applications. Proper installation ensures optimal performance. When installing a coaxial attenuator, it's crucial to use high-quality connectors to prevent signal loss. According to a 2023 report by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), improper connections can lead to a 20% reduction in signal integrity. Ensuring a tight, consistent connection minimizes this risk.
Routine maintenance is vital for coaxial attenuators. Regular checks for wear or damage can prolong their lifespan. It’s important to examine the housing for any signs of corrosion, as this can significantly affect performance. A 2022 study published by the Communications Society found that corrosion can lead to a signal degradation of up to 30%. Documenting these maintenance checks can make identifying patterns easier. Reflecting on the common oversight of neglecting routine checks can prevent larger issues down the line.
Finally, remember that environmental factors play a role in coaxial performance. Exposure to extreme temperatures or humidity can affect functionality. Aim to install attenuators in well-ventilated, climate-controlled areas whenever possible. According to recent data, optimal conditions can boost reliability by 15%. Recognizing these nuances is crucial for maintaining effective communication systems.
Article Source:
Developed and Managed byInfocom Network Private Limited.
 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry
